All home air conditioning systems rely on refrigerant for the cooling process that keeps residential spaces in Florida at comfortable temperatures throughout the year.
This unique substance must meet certain safety requirements and should be handled only by licensed professionals as it can be hazardous. There is also considerable attention on the environmental impact of refrigerants, especially concerning global warming.
Several types of AC refrigerants are available in Florida—but which one is appropriate for use in home AC?
The answer to this question and more information about AC refrigerants is found below…
What type of AC refrigerant is used at home?

STAY COOL ALL YEAR ROUND WITH ONE WAY AIR…
The team at One Way Air installs, services, and repairs all types of air conditioning systems in Southwest Florida. Get in touch with us here for a quote or call 239-233-4356 in emergencies.
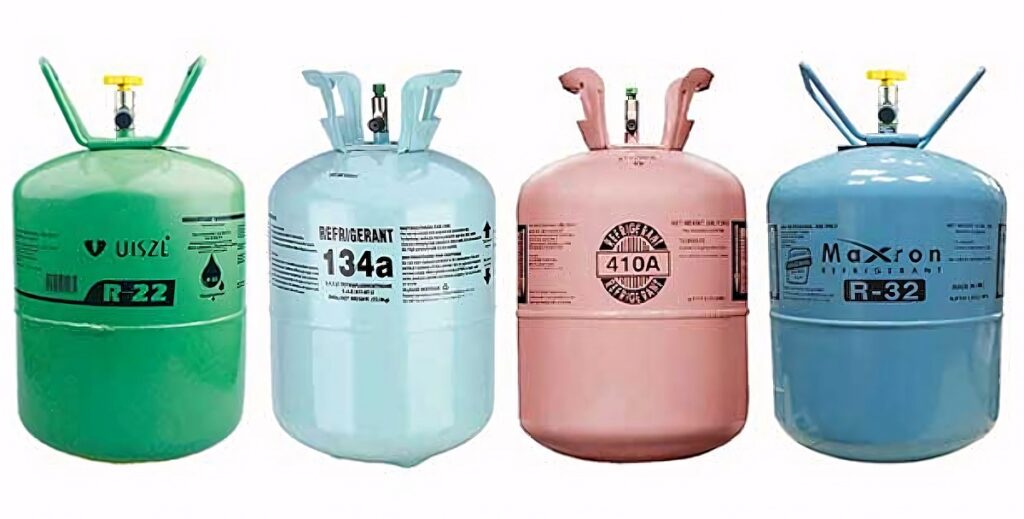
The answer is a little more complicated than you might expect. If your home air conditioner was manufactured after 2010, it likely uses a type of refrigerant known as Puron or R-410A. Even some air conditioners installed before that year use this colorless, odorless, non-flammable gas—but it is already being phased out.
Puron, which is instantly recognizable by its pink canister, was developed in 1991 to replace an older type of refrigerant called Freon or R-22. Research suggested that the hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) released by Freon were harmful to the environment, damaging the ozone layer.
However, soon after the new “environmentally friendlier” refrigerant, Puron, was introduced, further research suggested that it too could impact global warming. Additionally, the refrigerant is not very energy-efficient and can still be hazardous if it leaks during maintenance or repair work.
Both Puron and Freon contain fluorocarbons (Puron contains no chlorine though) and both are now viewed as having a potential negative effect on global warming.
The phasing out of Puron is already underway but is taking longer than expected. It’s certainly going to be around for a long time yet and most AC systems sold today still use it. However, as Puron is phased out, next-gen refrigerants like R-32 and R-454B will increasingly be used in new home air conditioners in Florida.
Different manufacturers may start to use these different refrigerants known as low global warming potential (“low-GWP”) blends and market them as “environmentally friendly” options.
These alternatives are also referred to as A2L refrigerants. A2L is a refrigerant safety classification assigned by ASHRAE—the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers.
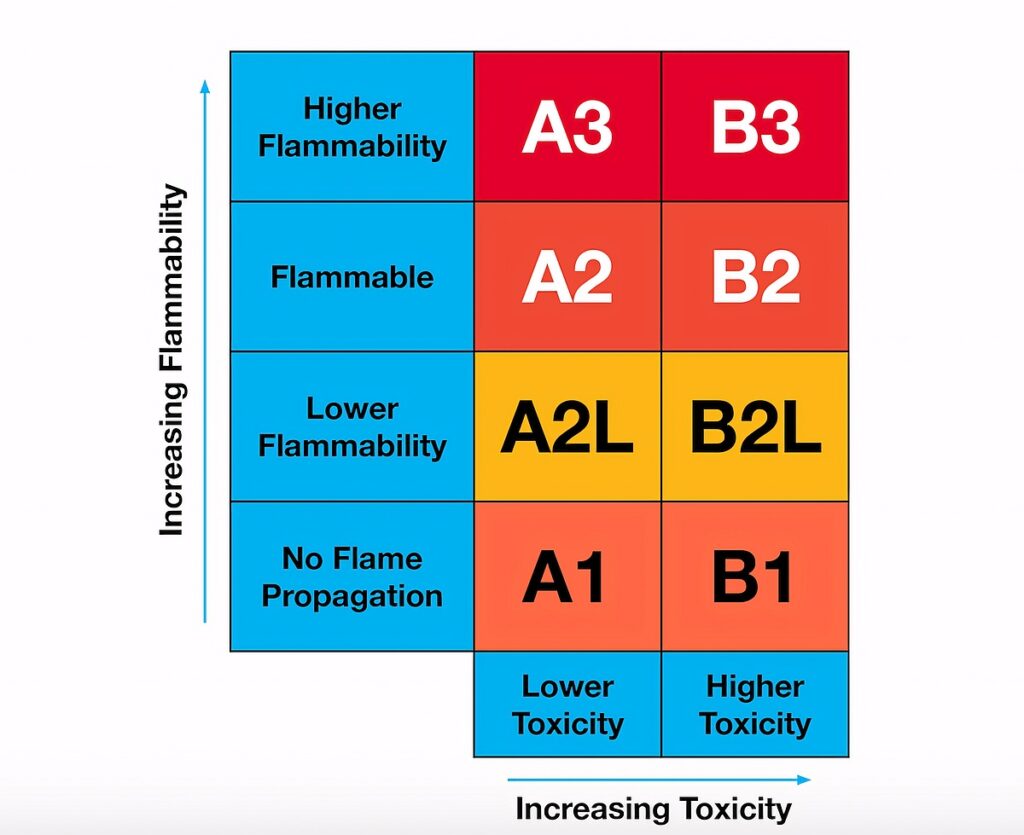
ASHRAE assigns an identifying reference letter and number to each refrigerant, which classifies the refrigerant according to the hazard involved in its use. “A” designates low toxicity while “2L” designates mild flammability.
What is AC refrigerant and why is it needed for home air conditioning?
Air conditioning works because of a complex system of heat exchange that involves several components all working together. If one or more components develop a problem, it can result in a less efficient AC unit or no cooling at all.
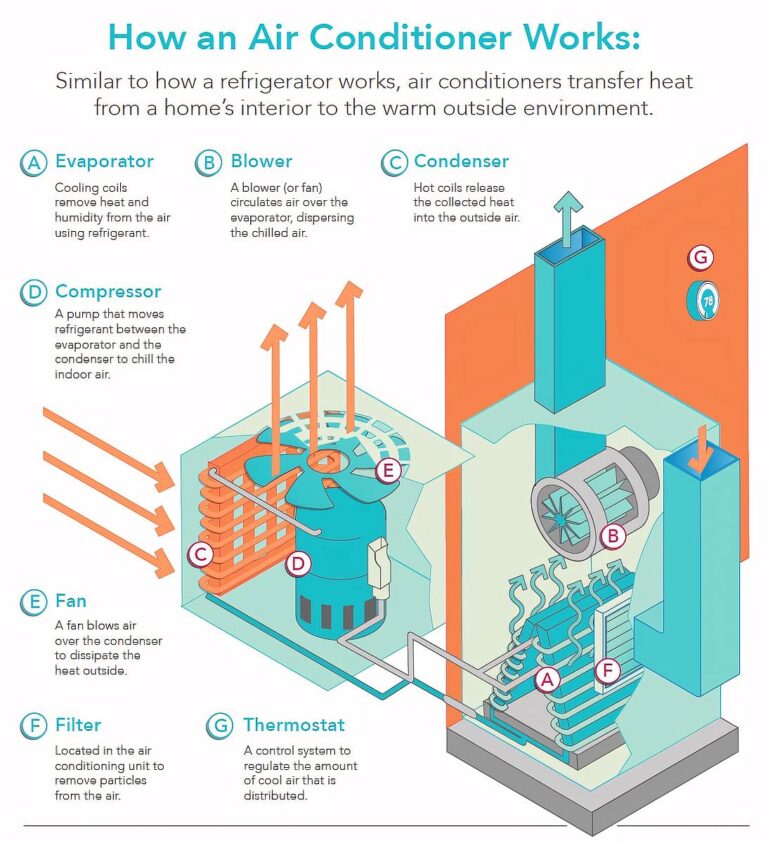
Refrigerant is essential for the heat exchange process, removing heat from the indoor air when temperatures are high. Its unique response to heat and pressure is responsible for its key role in the process, changing states between liquid and gas very quickly.
Without refrigerant, your central AC would just blow hot air around your home. Cool air wouldn’t circulate through the home’s ductwork and vents.
In a properly functioning central AC system, warm air from indoors enters the AC and passes over the evaporator coils, which contain the refrigerant. Within the coils, the refrigerant changes from a low-pressure gas to a high-pressure liquid in a closed system. The refrigerant absorbs the heat.
As the heat from indoors is absorbed, the refrigerant becomes liquid and is sent outside to the outdoor AC unit. This is responsible for cooling and it returns the refrigerant to its gaseous form. Fans in the AC unit help to cool the refrigerant so it can repeat the heat absorption process until the correct temperature is reached, as per the thermostat settings.
What other types of AC refrigerants are used in Florida?
Here’s a quick rundown of other refrigerants besides Puron that you’re likely to come across in Florida if you look hard enough…
Freon (R-22)
The AC refrigerant used in air conditioning systems in Florida made before 2010 was Freon or R22. This was easily recognized by its green canister and it was used for many decades since it was first produced in 1928.
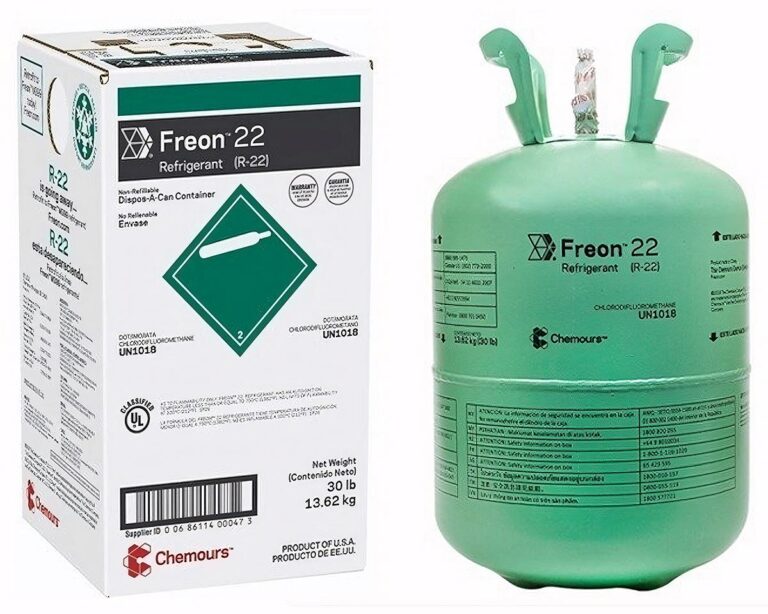

There are still plenty of home ACs that use Freon, as well as more modern Puron-based AC systems. However, since 2020, there has been a complete ban on the import or manufacture of R-22. Refills can only be done with stockpiles and recycled refrigeration liquid.
R-32 refrigerant
R-32 has been used as one of the replacement refrigerants for Freon but is far less common than Puron in home AC systems at present. It is generally considered the most balanced refrigerant in terms of environmental impact, energy efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness.
Another odorless gas, R-32 is increasingly found in modern AC units, with a significantly reduced impact on the ozone layer than its predecessors.
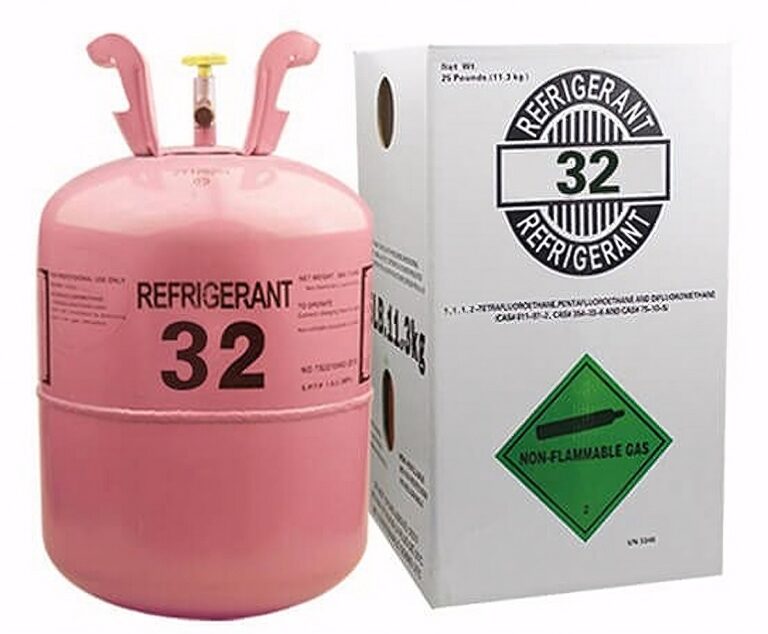

R-454B refrigerant
R-454B is another of the refrigerants used in newer AC units to replace the use of Puron due to its environmental friendliness. This refrigerant is used widely in heat pumps and commercial chillers and is known for its reliable performance.

R-134a refrigerant
R-134a is used worldwide in residential air conditioners, as well as automotive and commercial air conditioning systems. This substance is a hydro-fluorocarbon (HFC)-based gas, without any chlorine (similar to Puron).

Safety considerations when handling AC refrigerant
Some AC refrigerants pose safety threats and, generally speaking, they should only be handled by licensed professionals.
The safety threats center on the following:
- Toxicity
- Flammability
- Asphyxiation
- Physical hazards
Despite these safety issues, AC equipment manufacturers have created air conditioning systems that mitigate the hazards. New A2L refrigerants like R-32 are considered less hazardous than their predecessors too.
Tips for handling refrigerants
AC refrigerants should only be handled by licensed professionals. They are normally transported under pressure in gas cylinders.
Following are some basic tips for the storage and handling of refrigerants:
Storage
- Do not expose cylinders to temperatures above 113ºF
- Store as a compressed gas.
- Keep it in a well-ventilated place
- Keep away from open flames, hot surfaces, and other sources of ignition
- In case of a leak, prevent sparks and open flames
Safety measures
- Wear eye protection and insulated gloves
- Wear protective clothing if there is a possibility of direct contact or splashes
- Wear safety boots when handling refrigerant cylinders
- Never lift a cylinder by the top valve
- When moving cylinders, keep their caps on
- Always assume that the cylinder contains gas
- Wear self-contained breathing apparatus in high gas concentrations
- Provide good ventilation

Regulations for the use of AC refrigerants in Florida
Under the U.S. Clean Air Act and the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer, the U.S. phased out the use of CFCs in the 1990s and is currently phasing out the use of HCFCs.
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA):
“These chemicals eventually reach the stratosphere where they deplete the stratospheric ozone layer. The ozone layer helps protect us from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation that can cause skin cancer and cataracts.”
This has severely affected the use of AC refrigerants. The use of refrigerants with lower pollutant levels has also prompted changes to the design of cooling systems, coinciding with the development of equipment offering greater efficiency in many cases.
The latest push has been for a move toward the types of A2L refrigerants described above.
Disposal
AC refrigerants must be disposed of carefully to prevent accidents and environmental harm. This is also required under the provisions of the Clean Air Act and failure to follow the rules can result in hefty fines. You can read more about disposing of AC equipment and refrigerants here.
If you’re considering a new AC installation and are unsure about compliance with local regulations in Florida, speak to an AC professional at One Way Air for a rundown of your options.

FAQs
What is the most environmentally friendly AC refrigerant?
New AC systems are increasingly using A2L refrigerants like R-32, which are considered less hazardous than their predecessors and less likely to contribute to global warming. Here is a full list of acceptable substitutes for residential AC systems.
How can I find out what kind of refrigerant my home AC contains?
The refrigerant used in a home AC should be listed on the unit’s nameplate, which is usually positioned on the outdoor condenser unit. If not, it should be in the manual that was issued with your AC unit or you can speak to the company that supplied your unit or performs AC maintenance.
What does “low refrigerant charge” mean?
You may hear the term “low refrigerant charge” when troubleshooting AC problems or you are getting your AC system serviced.
A low refrigerant charge simply means that your unit is low on refrigerant. If that happens, it likely points to a deeper issue, such as a cracked coil and a refrigerant leak.
AC operates as a closed system and should not lose any refrigerant under normal circumstances. A low refrigerant charge can lead to several issues, such as AC running but not blowing cold air and it can be hazardous as many AC refrigerants are toxic.
How do I know if I have low AC refrigerant levels?
Puron, like most AC refrigerants, is a non-toxic gas that lacks odor, so leaks can be difficult to detect. Some common signs of low AC refrigerant levels include:
- Refrigerant lines making bubbling or hissing noises
- Lack of home cooling despite the AC running
- Ice on the refrigerant lines
- Higher energy bills
It’s important to arrange an inspection if you notice any of these signs of a low refrigerant charge. You may need AC repairs that may become more costly if you wait to act.
What should I do if my home AC uses old refrigerant?
Air conditioning systems run best using the refrigerant that they were designed for. The use of new refrigerants often prompts design changes in the components used in AC systems so if your AC uses Puron, you’ll need to top it up with Puron if it develops a leak.
When the time comes to replace your AC unit, consult with AC professionals at One Way Air to select an energy-efficient system that uses one of the non-ozone-depleting alternatives.
Remember, at present, you’re not breaking any rules by running a Freon-based AC system and you can still top up systems with existing stockpiles of the refrigerant.
Does changing the refrigerant require new refrigerant lines?
Usually, an AC system that’s been upgraded to an environmentally friendlier solution can use the existing refrigerant lines. These insulated copper lines must be of the right diameter specified by the AC equipment manufacturer and all traces of the old refrigerant and oils must be removed.

AC tune-ups and repairs in SWFL
Air conditioning costs are high in Florida and it’s important to maintain an efficient system both for your comfort and your pocket.
If you’re in SWFL and have any issues with your cooling system, contact One Way Air to arrange a full inspection and a tune-up or repairs to prolong the life of your AC.